|
UNECE R155 might be not prime of thoughts for many informal observers
of the automotive {industry}. Nevertheless, for these inside it’s
producing loads of discourse and producing elementary questions
as to what unique gear producers' future competencies
must be. For these exterior the {industry}, the closest encounter
with R155 might be the information that Porsche ceased the sale of its
inside combustion engine (ICE) Macan in Europe early in 2024
due to compliance points.
Due to this one might be forgiven that it’s one other
electrical automobile mandate. However no, R155 is all about cybersecurity.
Not simply cybersecurity at a automobile's begin of manufacturing, however
all through its end-to-end life cycle.
The rising connectivity of automobiles is bringing extra
vulnerabilities. A mini-industry has sprung up that exposes the
frailties of immediately's automobiles via a sequence of audacious hacks.
Among the many well-known hacks are the instance of the Nissan Leaf within the north of England being
remotely managed from a poolside in Australia or Tencent's Eager Safety Lab hack of Tesla fashions
again in 2016. R155 is designed to reduce the frequency
of such incidents.
The regulation requires systematic measures akin to common danger
assessments, penetration assessments and sturdy incident response
mechanisms to mitigate cyberthreats. The regulation additionally emphasizes
a safe software program replace administration system to keep up automobile
security with up-to-date software program.
The R155 regulation* has implications past in-vehicle
issues, requiring in depth organizational effort and
probably excessive prices. Managing danger all through the automobile life
cycle will be difficult, notably for conventional OEMs with a
big selection of auto fashions. Consequently, OEMs at the moment are targeted on
embedding safety into automobile design and making certain compliance to
keep away from penalties and withdrawal of auto homologation.
The transition to a compliant Cybersecurity Administration System
(CSMS) presents challenges and value issues for OEMs. In a
current estimation by S&P World Mobility, the prices of
compliance for 2 automobiles designed with older design distributed
E/E architectures have been calculated for an A-segment automobile and a
premium D-segment automobile. The implementation prices on present
fashions can simply exceed $1 million even for the A-segment automobile
with fewer options. Thus, withdrawing automobiles from sale which might be
approaching finish of life or are offered in low quantity makes excellent
sense.
To this point, the Porsche Macan has been the one automobile formally
retired due to R155 and there was a lot hypothesis within the
press with 9 particular automobiles extensively cited as impacted. To
confirm the studies, we sought the counsel of colleagues in S&P
World Mobility's manufacturing forecasting division. Primarily based on this,
we are able to affirm that of the 9 automobiles reported, 5 are
particularly impacted by the R155 regulation. The affected automobiles
are three Porsche fashions (Boxster, 718 Cayman and Macan) and two
Audi fashions (R8 and TT). None of those fashions will proceed to be
offered in Europe owing to the regulation. Nevertheless, gross sales of those
automobiles could proceed in areas exterior of Europe that aren’t
topic to the laws.
Within the midterm, OEMs can’t discontinue all legacy platforms,
nonetheless, they usually should bear the price of making automobiles compliant,
particularly high-volume platforms which might be deliberate to proceed for
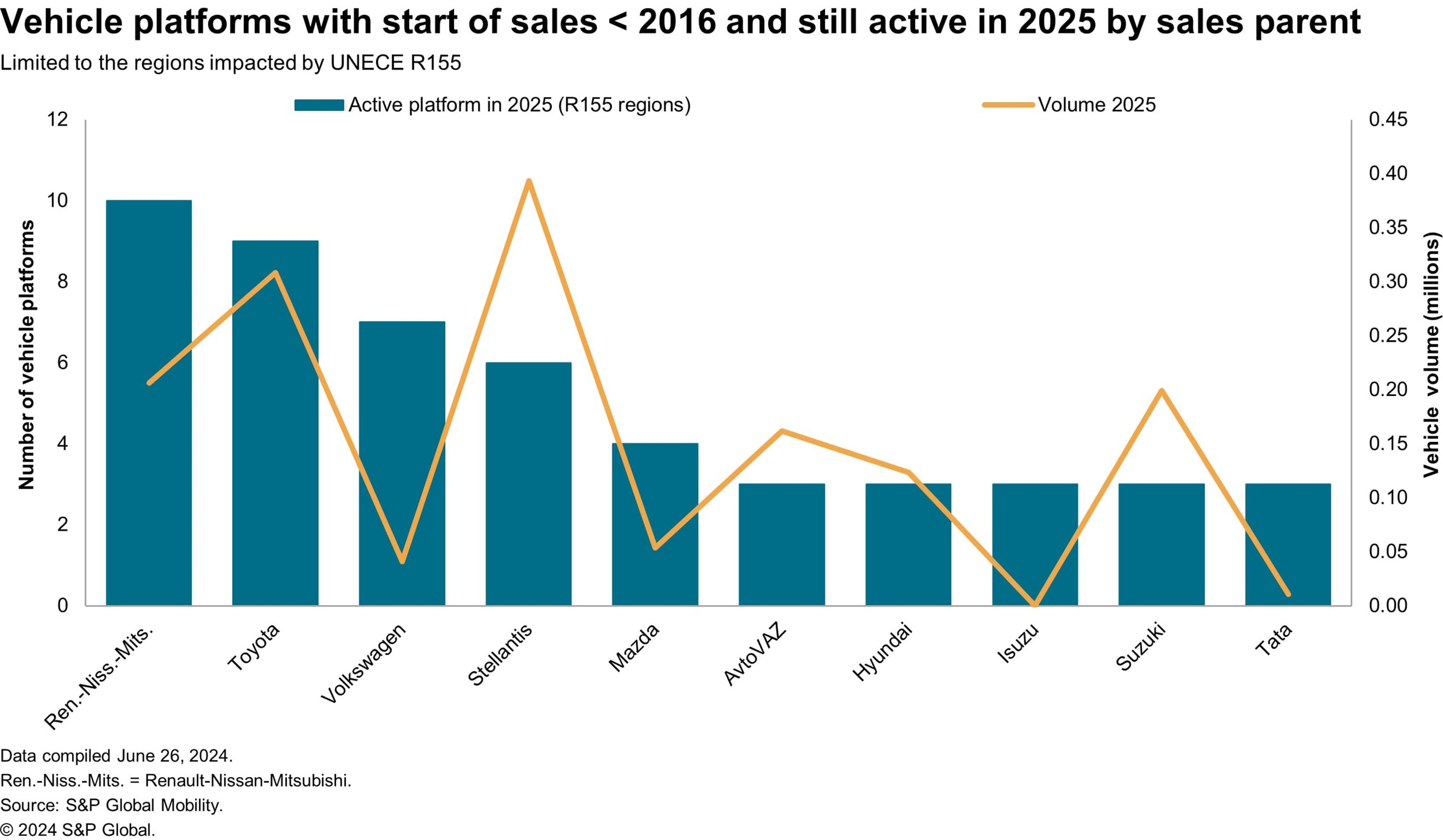
a number of years. The next chart shows the relative publicity
of OEMs to those “retrofit” compliancy prices. It reveals the quantity
of platforms nonetheless in manufacturing in 2025 with SOP sooner than
2016, i.e., earlier than most OEMs began contemplating cybersecurity in
design.
Nevertheless, OEMs are much less tactical and are rethinking the best way they
design automobiles as they make them software-defined automobile
(SDV)-ready. Deploying SDV-ready automobiles supported by superior E/E
architectures, notably centralized zonal structure that may
deploy software program updates seamlessly, avoids the pricey retrofitting.
In addition they guarantee compliance with laws because the
system-on-a-chip (SoC) powering them are geared up with embedded
crypto and safety capabilities compliant with R155.
As with the SDV and lots of the different {industry} megatrends,
cybersecurity has introduced plenty of navel-gazing amongst {industry}
contributors. There are elementary inquiries to reply as to what
the core competencies of the OEMs and tier 1s must be within the
future. They’re uncertain, for instance, whether or not software program improvement
and SDV stacks ought to depend on outsourcing or to maintain sure
facets in-house. The best way to add cybersecurity compliance can also
current conflicts with an OEM's chosen software program path on the
elementary make or purchase resolution. The corporate that has chosen the
make path could discover hidden prices with cybersecurity compliance such
as including in-house experience and the price of working Safety
Operation Facilities in-house.
Both approach, R155 and cybersecurity obligations are posing new
challenges that have to be addressed. Whereas there could also be headlines
about manufacturing runouts in Europe, the main focus is on navigating
these new roadblocks.
*Adopted by the United Nations Financial Fee for
Europe (UNECE), the UN R155 turned efficient in January 2021. This
regulation mandates that each one new automobile sorts should comply beginning
from July 2022, and all automobiles produced should comply by July
2024.
Subscribe to
AutoTechInsight
|




