Regardless of infrastructure and manufacturing challenges that would
mood the tempo of electrical automobile (EV) adoption, India’s giant
home market, low present EV penetration charges, and growing
manufacturing capability make it a horny vacation spot for
automakers and suppliers.
If Tata Motors’ and Mahindra’s success in navigating the
pandemic and semiconductor shortages are any indication, India is
anticipated to turn out to be a serious participant in international gentle automobile
manufacturing. Moreover, with international provide chain disruptions and
the return of protectionism, India’s place as an export base for
mature markets is turning into more and more viable.
Bridging Gaps In World Provide Chain
 Supply: S&P World Mobility Mild
Supply: S&P World Mobility Mild
Car Manufacturing Forecast
India’s Resilient Automotive Sector
Whereas main markets like mainland China, the USA, and
Germany grappled with manufacturing setbacks throughout disruptions brought about
by COVID-19 and semiconductor shortages, India’s automotive sector
confirmed resilience. Indian OEMs demonstrated a stronger functionality
to safe semiconductor provides regardless of having decrease buying
energy in comparison with international automobile producers and providing fewer
options of their autos.
India’s excessive GDP development fee, which is additional projected to
stay over 6% between 2026 and 2031, considerably larger than the
international common of two.7%. India’s home market is a major
draw for international automakers. Because the third largest market in gentle
automobile gross sales and the 4th largest in gentle automobile manufacturing,
India’s low automobile penetration fee of simply 38 autos per 1,000
individuals presents a large development alternative. In line with S&P World Mobility Mild
Car Manufacturing Forecasts, manufacturing capability is predicted
to rise from 6.8 million items in 2023 to 10 million by 2031,
additional solidifying India’s position within the international automotive
panorama.
Concurrently, the US and EU’s elevated tariffs on Chinese language EVs
have created a void that India is well-positioned to fill. With its
secure provide chain, gentle automobile manufacturing development in India is
anticipated to keep up a gradual tempo. S&P World Mobility
initiatives a development fee of 4 p.c for 2024, with longer-term
expectations of development stabilizing between 4% and 6% yearly
via 2031.
A major driver of this development is the anticipated improve
in exports from main producers like Maruti Suzuki and Hyundai
which can profit from the rising demand for reasonably priced autos
in rising markets.
Suzuki, for instance, goals to ramp up manufacturing to 4 million
items by 2031, with a deal with hybrids and EVs.
XEV Transformation: India
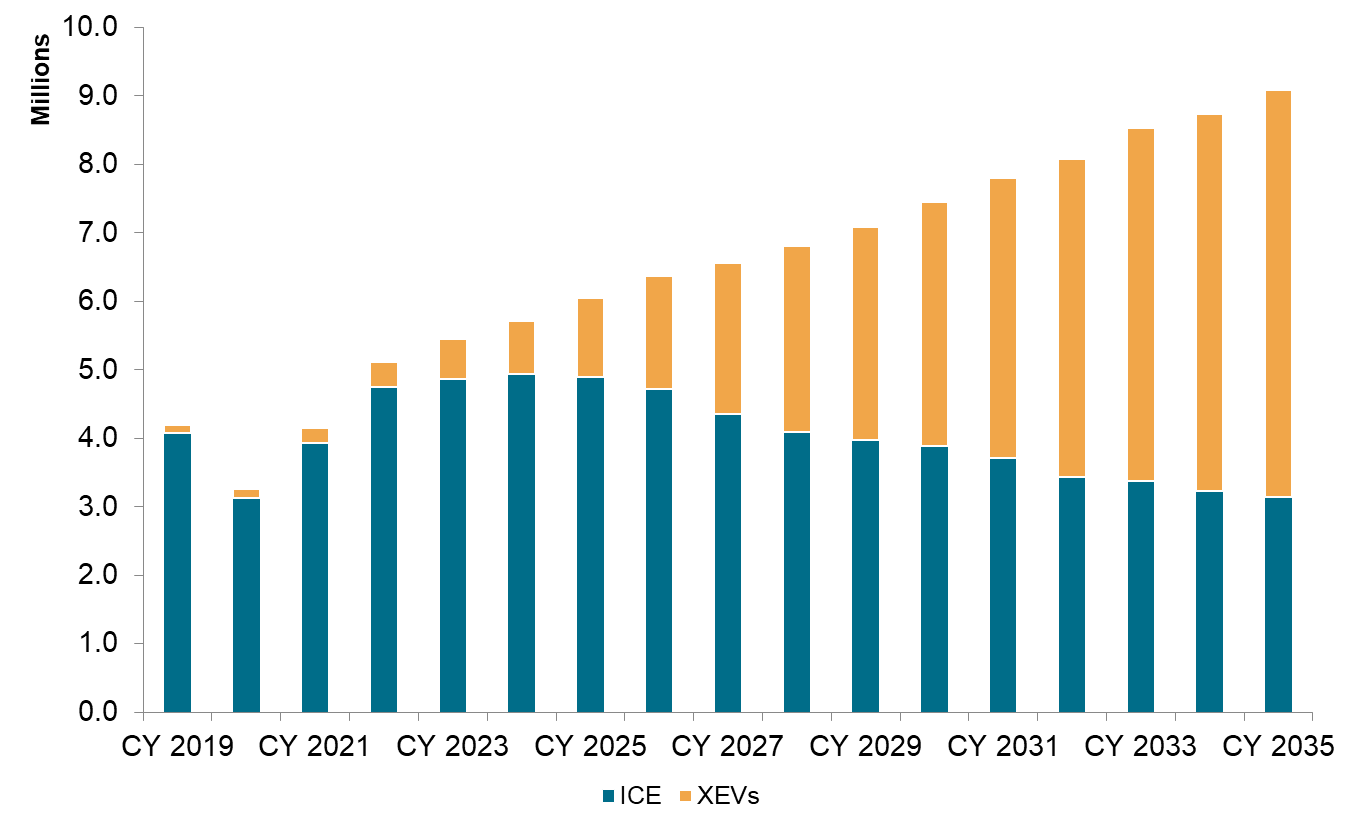
Information compiled: eighth July 2024.
Supply: S&P World Mobility.
XEVs = Gentle Hybrid electrical automobile (MHEV)+ Hybrid
electrical automobile(HEV)+Plug in Hybrid automobile (PHEV)+Vary extender
electrical automobile (REX)+Battery Electrical Car (BEV)
Transition to Clear Applied sciences
India’s automotive panorama can also be shifting in direction of EVs. The
share of inner combustion engine (ICE) autos produced in
India is projected to lower dramatically, from 97% in 2019 to
round 35% by 2035. The implementation of stricter emission
requirements just like the Bharat Stage 6 (BS6) and upcoming BS 7 norms
have pushed producers to innovate and transition in direction of
cleaner applied sciences.
The market can also be witnessing a corresponding rise within the
adoption of low emission autos like XEVs. Demand for hybrid
electrical autos (HEVs) and battery electrical autos (BEVs) is
anticipated to develop considerably, with a notable improve in hybrid,
vary extender autos and plug-in hybrid autos within the quick
time period.
Nevertheless, the present state of infrastructure, significantly the
availability of charging stations and the general EV ecosystem in
India might mood the tempo of EV adoption. Customers and
automakers are nonetheless considerably cautious within the present EV panorama.
There’s a famous delay in adopting new fashions and platforms because of
uncertainty surrounding regulatory circumstances, just like the
aforementioned BS7 emission norms.
Excessive prices related to early-stage EV manufacturing have
additionally led to rising automobile costs, elevating issues about
affordability amongst first-time patrons. The rise in reductions
for ICE autos amid client trepidation and excessive stock
ranges might additional gradual the speed of adoption within the speedy
future.
Even with these mid-term pressures, the pattern is unmistakable.
Car producers in India are more and more adopting
multi-energy platforms that may help each inner combustion
engine (ICE) autos and EVs. Over the following few years, these
platforms are anticipated to extend available in the market, setting the stage
for the eventual rise of devoted EV platforms. Total, the
long-term outlook for EVs in India is optimistic. As infrastructure
improves and client issues are addressed, EV adoption is probably going
to speed up, in line with S&P World Mobility forecasts.
Because the automotive business is within the midst of a technological
revolution, there may be additionally a heightened emphasis on provide chain
administration. Improvements like ADAS (Superior Driver Help
Programs), software-defined autos, and AI (Synthetic
Intelligence) have gotten customary options, which require OEMs to
combine these parts into their provide chain.
This text is a part of a sequence that includes highlights from
S&P World Mobility’s 2024 Options Webinar Collection. The
webinar, India’s Mild Car Manufacturing Outlook and Tata Motors’
Provide Chain Resiliance, occurred on July 16, 2024.
This text was revealed by S&P World Mobility and never by S&P World Rankings, which is a individually managed division of S&P World.




